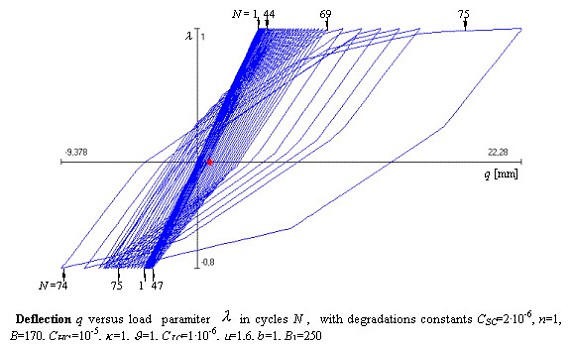
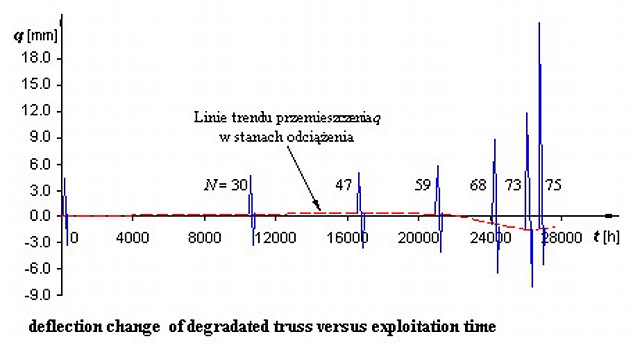
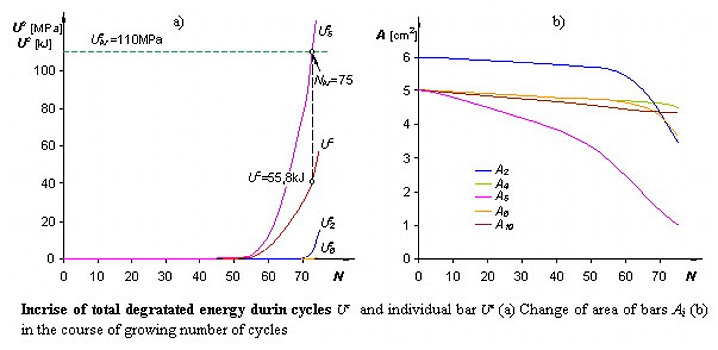
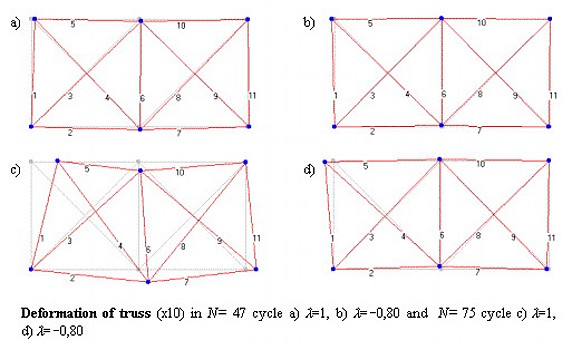
CSM w zastosowaniach przemysłowych
Zerowymiarowe obliczenia CSM dotyczą nowych metod szacowania żywotności konstrukcji związanej z degradacją własności materiału wywołaną niskocyklicznym zmęczeniem mechanicznym i termicznym korozją naprężeniową, pełzaniem wysokotemperaturowym oraz adaptacją sprężysto-plastyczną.
Life time computations of corrosive structures undergoing exploitation cycles
Researches are based on our in-house code D-KRAT based on the algebraic 0D model of mass, momentum and energy balances extended by additional evolution equations for the following physico-chemical phenomena:
 Thermal deformations
Thermal deformations- Cyclic plasticity and reattaching
- High temperature creep
- Stress/thermal induced phase transitions
- Hydrogen, oxygen and carbon generated chemical reaction/diffusion
- High temperature stress corrosion
- Low cyclic corrosion
- Electrochemical corrosion
- Hydrogen ductility
- Environmental interaction with surrounding fluid via electrochemical potential and pH
- Low cyclic fatigue
- Low cyclic damage evolution as a synenergic effect of chemical reaction products, mechanical and thermal loading during a real exploitation cycle.
D-KRAT code is especially dedicated for on line numerical simulation of the referential state of structures in real exploitation cycle, which consist four main elements:
- start-up
- nominal work
- shut-down
- stay
More information [ukryty email]